Sports Field Lighting Requirements and Design

Directory:
1. Competition Events and Venues Introduction
2. Opportunities and Challenges in Lighting Engineering Construction
2.1 Retrofit and Use of Existing or Ongoing Venues
2.2 Widespread Use of LED Lighting Technology
2.3 Rapid Advancements in TV Broadcasting Technology and Demand
2.4 Advancements and Implementation of Intelligent Lighting Technology
Sports field serve as crucial infrastructure for hosting and organizing events, with lighting playing a vital role in ensuring the success of these events and their broadcasts. The effective construction of lighting systems in sports field is essential for the seamless execution of competitions and high-quality media coverage, allowing millions of viewers to share in the excitement of sports while also boosting the city's global presence. This article will explore the integration of competition events and venue construction plans, focusing on the extensive use of LED technology, intelligent lighting, ultra-high-definition, and ultra-slow motion broadcasting in sports. It will also address the opportunities and challenges these technologies present for venue construction, emphasizing the principles of "green, intelligent, frugal, and civilized" competition, and outlining the requirements for developing and implementing sports field lighting.
1. Competition Events and Venues Introduction
There are 40 competition events categorized as follows:
Indoor events: swimming, badminton, basketball, boxing, cycling, fencing, gymnastics, handball, judo, shooting, table tennis, taekwondo, volleyball, weightlifting, wrestling, karate.
Outdoor events: track and field, football, hockey, modern pentathlon, rugby 7. tennis, competitive rock climbing, baseball, and softball.
Other events: archery, canoeing, equestrian, golf, rowing, sailing, triathlon, martial arts, sepak takraw, jiu-jitsu, jujitsu, roller skating, kabaddi, squash, cricket, chess.
As a comprehensive sports event, there is a wide variety of competition events, each with distinct venue requirements, competition characteristics, and broadcasting needs, which places significant demands on lighting design and management. Additionally, the limited experience in constructing and managing venue lighting projects presents further challenges for the lighting implementation at the Hangzhou Asian Games venues.
2. Opportunities and Challenges in Lighting Engineering Construction
The quality and effectiveness of lighting are key indicators for assessing a sports field's quality. With rapid advancements in society and technology, the demand for event broadcasting has become increasingly diverse and personalized. Technologies such as LED, intelligent lighting, ultra-high-definition, and ultra-slow motion broadcasting are now prevalent in sports events. The trend of multi-camera coverage and comprehensive broadcasting both inside and outside the stadium is on the rise. A significant technical challenge for event organizers and constructors is how to leverage intelligent lighting technology to synchronize and integrate functional and atmospheric lighting for events.
2.1 Retrofit and Use of Existing or Ongoing Venues
In the design of sports lighting, the placement of lamps plays a crucial role in the effectiveness and quality of lighting projects. The positioning of lights on the horse track is particularly important for sports lighting. Incorrect lamp placement can significantly diminish both the quality and quantity of illumination, while also leading to increased energy consumption. Existing or renovated venues are typically not specifically designed for particular events. Factors such as site conditions and lamp installation locations can complicate the design and execution of the venue's lighting project, raising the technical challenges and imposing stricter requirements for the management and organization of stadium lighting.
2.2 Widespread Use of LED Lighting Technology
High-pressure gas discharge lamps and metal halide lamps have several drawbacks as lighting sources. In contrast, LED lighting offers benefits such as low energy consumption, adjustable color quality, flexible control, and instant start-up, making it a popular choice in sports lighting. This stadium will utilize LED lighting products.
2.2.1 Color Rendering Index of LED Lamps
Inspection data indicates that nearly 40% of the lamps have a color rendering index exceeding 90. while about 57% have a color rendering index below 80.
2.2.2 Beam Angle of LED Lamps
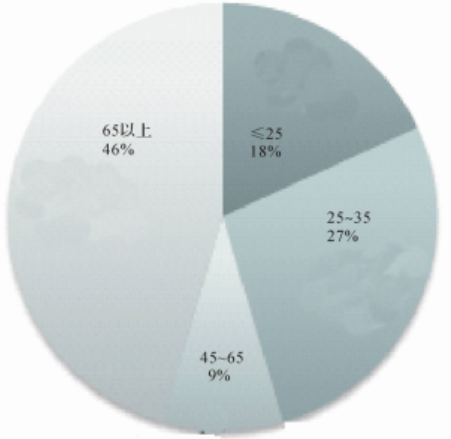
A beam angle that is too wide can lead to ineffective use of the lamp's luminous flux, resulting in the issue of "seeing light but not seeing far," which means that vertical illumination at a distance may not meet standard requirements. When accounting for television broadcasting needs, it is essential to strictly control the beam angle of sports lighting lamps. Over 50% of the tested LED lamps have a beam angle greater than 45°, as illustrated in Figure 1.
fig1 LED sports lighting beam angledistribution
2.2.3 Flicker in LED Lamps
LED lamps, particularly high-power ones, exhibit significant advantages regarding flicker performance. Over 93% of the lamps tested showed a flicker ratio below 6%, and more than 86% had a flicker ratio of 1% or less. However, if the power supply for these LED lamps is poorly designed, the flicker issue can become more pronounced than with traditional light sources, potentially exceeding 40%. The test results confirm that LED lighting technology is suitable for sports lighting. Nevertheless, ensuring that product quality aligns with project requirements will pose an additional challenge for the lighting management and construction of venues for the Asian Games.
2.3 Rapid Advancements in TV Broadcasting Technology and Demand
Sports events are primarily created for television broadcasting. The evolution of broadcasting technology and the increasing demand for broadcasts significantly influence the promotion of sports events, while also imposing higher standards and challenges on the construction of sports field lighting projects.
2.3.1 Fast-Paced Advancements in TV Broadcasting Technology
With the swift progress in electronic technology, new broadcasting methods such as ultra-high-definition (UHD) TV and ultra-slow motion filming have been increasingly utilized in sports event broadcasts, enhancing the viewing experience for audiences. This has also become a crucial focus for sports lighting engineering:
(1) Ultra-high-definition TV broadcasting involves using UHD technology for live shooting, production, transmission, and broadcasting of programs. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has defined UHD-1 (resolution of 3840×2160) and UHD-2 (resolution of 7680×4320), commonly known as 4K and 8K, respectively. UHD TV offers higher resolution, increased frame rates (up to 120 frames per second), and a broader dynamic range (10 bits or even 16 bits), providing a richer audiovisual experience for viewers.
(2) "Super slow motion" (SSM) filming captures footage at speeds exceeding three times the normal rate (75 frames per second), often reaching 300-600 frames per second, and even up to 900 frames per second. This technique allows for a more detailed portrayal of the rapid, high-intensity moments in competitive sports, offering TV viewers an experience that surpasses what they would see live.
2.3.2 Evolution of Broadcasting Requirements
At present, sports television broadcasts offer more diverse content, shifting from a focus solely on professionalism to a blend of entertainment and professionalism. The scope of content has expanded from a core focus to a broader range. This evolution has introduced new demands for live broadcast production, leading to an increase in the variety of camera angles and broadcast equipment used for sports events. This allows for the capture of exciting moments from multiple perspectives, catering to the diverse and personalized viewing preferences of various audience segments. However, this also raises the bar for the design and execution of lighting projects in sports field.
2.4 Advancements and Implementation of Intelligent Lighting Technology
Technological advancements have propelled sports lighting towards greater networking, digitization, and intelligence. While maintaining high-quality lighting standards, these developments can significantly lower energy consumption and enable more precise management of outdoor lighting.
The current world is experiencing the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by rapid technological advancements and significant transformations. Social and economic shifts, along with advancements in science and technology, have led to a growing demand for diverse and personalized broadcasting experiences. The development and management of sports field will focus on key areas such as the integration of functional and atmospheric lighting for events. The following specific measures will be implemented:
(1) Define the lighting needs of sports field
We will further specify the functional requirements of the venues based on their actual conditions, establish lighting standards in line with TV broadcast plans and the venues' post-event functions, and set clear criteria for the quality of LED lighting products used. This will provide a standard framework and detailed acceptance criteria for the high-quality construction of lighting facilities.
(2) Enhance quality monitoring of venue lighting projects
We will improve quality control during the implementation phase by developing a monitoring technology system for venue processes, conducting technical reviews of lighting design plans, establishing appropriate technical parameters, increasing on-site supervision, and conducting thorough testing of lighting projects to ensure high-quality execution.
(3) Review and assess the Asian Games venue lighting project post-implementation
We will focus on summarizing and analyzing the experiences gained from the implementation and construction of venue lighting. By evaluating the effectiveness of lighting projects during events, we will compile relevant insights that will aid in the preparation and construction of large-scale events and contribute to the ongoing advancement of lighting technology.